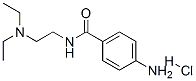
7699-39-0
- Product Name:PROCAINAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
- Molecular Formula:C13H22ClN3O
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:271.79
Product Details;
CasNo: 7699-39-0
Molecular Formula: C13H22ClN3O
Buy High Quality Top Purity PROCAINAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE 7699-39-0 In Medicine
- Molecular Formula:C13H22ClN3O
- Molecular Weight:271.79
- Melting Point:165-168 °C
- PSA:58.36000
- LogP:3.11450
PROCAINAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE (Cas 7699-39-0) Usage
|
Description |
Procainamide hydrochloride is a common pharmaceutical substance. It is classified as a Class IA anti-arrhythmic medication. |
|
Uses |
In animal studies, specifically in rats, procainamide hydrochloride has been found to reduce cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. This is evidenced by the normalization of certain liver enzyme activities (plasma activity of glutamic oxalacetic transaminase and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase) and histological examination of liver tissue. It is used to manage and treat certain types of cardiac arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) by affecting sodium channels in cardiac cells. |
7699-39-0 Relevant articles
Anomalous Electrical Conductivity Behavior at Elevated Pressure in the Protic Ionic Liquid Procainamide Hydrochloride
Z. Wojnarowska, C. M. Roland, A. Swiety-Pospiech, K. Grzybowska, and M. Paluch
, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 015701 – Published 5 January 2012
Using broadband dielectric spectroscopy, we investigated the effect of hydrostatic pressure on the conductivity relaxation time τ σ of the supercooled protic ionic liquid, procainamide hydrochloride, a common pharmaceutical. The pressure dependence of τ σ exhibited anomalous behavior in the vicinity of the glass transition T g , manifested by abrupt changes in activation volume.
Reduction of cisplatin hepatotoxicity by procainamide hydrochloride in rats
Antonio Zicca a, Sergio Cafaggi b, Maria A Mariggiò c, Maria O Vannozzi d, Massimo Ottone d, Vittorio Bocchini e, Gabriele Caviglioli b, Maurizio Viale d
, European Journal of Pharmacology Volume 442, Issue 3, 10 May 2002, Pages 265-272
Here, we report that procainamide hydrochloride, at an i.p. dose of 100 mg/kg, reduces cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity, as evidenced by the normalization of plasma activity of glutamic oxalacetic transaminase and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, as well as by histological examination of the liver tissue.
Relevant Products
-
Tetracaine hydrochloride
CAS:136-47-0
-
2-Phenylacetamide
CAS:103-81-1
-
Adenosine 5'-monophosphate
CAS:61-19-8