70-18-8
- Product Name:Glutathione
- Molecular Formula:C10H17N3O6S
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:307.327
Product Details;
CasNo: 70-18-8
Molecular Formula: C10H17N3O6S
Appearance: White cryst. powder
Best Price Factory Sells Powder Glutathione 70-18-8 In Stock
- Molecular Formula:C10H17N3O6S
- Molecular Weight:307.327
- Appearance/Colour:White cryst. powder
- Vapor Pressure:0mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:192-195 °C (dec.)(lit.)
- Refractive Index:-17 ° (C=2, H2O)
- Boiling Point:754.492 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pK1 2.12; pK2 3.53; pK3 8.66; pK4 9.12(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:410.102 °C
- PSA:197.62000
- Density:1.441 g/cm3
- LogP:-0.72400
Glutathione(Cas 70-18-8) Usage
|
Features and functions |
Glutathione is composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine by peptide bonds condensation of three peptide compounds,which is the most important antioxidant stress of low molecular mercaptan in mammalian cells.We discovered it in 1921 and determined the chemical structure in 1930 , the famous American nutrition health experts said Dr Al sensitive del glutathione is three times the efficiency of the anti-aging amino acid, also known as the antioxidant master of nature, the appearance is colorless transparent thin granular crystal, it is soluble in water, dilute alcohol, liquid ammonia, dimethyl formamide,and it’s insoluble in ethanol, ether, acetone.Its solid character is stable, its aqueous solution is easy oxidized in the air for oxidized glutathione, widely exists in baker's yeast, wheat germ, animal liver, chicken blood, pig blood, tomato, pineapple, cucumber, of which is highest in the wheat germ and liver, content as high as 100~1000 mg/100 g.With antioxidant, scavenging free radicals, detoxification, enhance immunity, anti-aging, anti-cancer, anti radiation damage, and other functions.It also helps white blood cells to kill bacteria and prevent the oxidation of the vitamins C and E, to prevent stroke and cataract formation.In addition, glutathione can bind the carcinogen, than excrete them through the urine in vitro. The liver is the most important detoxification organs, which contains rich in glutathione (GSH) on the liver function such as synthesis, detoxification, estrogen inactivated protection.It is the first anti-oxidant that the human body is to counteract the damage of free radicals, and the free radical is a contributing factor to the aging and disease.When the liver is damage, such as suffering from all kinds of liver disease, the body will consume large amounts of GSH to help repair the injured liver and detoxification, that cause the body's glutathione are greatly reduced.But this time we need to take some glutathione peptide drugs, is advantageous to the injury of liver to repair itself.Thus, glutathione peptide drugs are suitable for viral hepatitis (hepatitis a and hepatitis b, etc.), alcoholic liver disease,drug-induced liver disease, fatty liver disease ,it’s a good medicine to protect liver. |
|
Three active peptide compound |
Glutathione (Glutathione, GSH) is made up of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine by peptide bonds condensation of three peptide compounds, chemical name called gamma-L-glutamine-L-in ammonia acyl-glycine, its structural formula is shown in figure 1. Structured from the figure, the GSH and other peptide and protein is different, it's a special peptide bond in the molecule,by glutamate gamma carboxyl (-COOH) and alpha amino-cysteine (NH2) peptidebond condensation. Figure 1 :Glutathione (GSH) chemical structural formula GSH biosynthesis is directly controlled by its synthetase, rather than as protein synthesis is conducted on the ribosome, glutathione biosynthesis includes the following two reaction, as shown in figure 2. Figure 2: The synthesis of GSH Hopkins first discovered glutathione as early as 1921 , than divided it into reduced glutathione (GSH) and oxidative type (GSSG) two kinds.GSH exists in all living cells, it’s higher in yeast, wheat germ and liver, 100~1000 mg/100 g.According to recent data, S.c erevisiae Jacqueline Nottingham-5-8 strains of GSH content of up to 3058 mg/3058 g.In dry yeast type oxidation GSH exists, and almost all people in red blood cells were reduced glutathione, GSH can be synthesized in the red blood cells.Glutathione molecule contains a lively mercapto-SH, susceptible to oxidative dehydrogenation, two molecules of reduced glutathione (GSH) into a molecular dehydrogenation oxidation type glutathione (GSSG).Peptide by oxidation type in two three disulfide bond together, which play an important physiological role in living organisms is reduced glutathione, GSSG as GSH is physiological activity. |
|
The physical and chemical properties |
Glutathione molecular weight of 307.33, melting point of 189~193 ℃ (decomposition), crystal is colorless transparent thin cylindrical in shape and isoelectric point of 5.93.It is soluble in water, dilute alcohol, liquid ammonia and methyl formamide, and insoluble in alcohol, ether and acetone.Organisms only with physiological activity, GSH and GSSG need to restore to play its important physiological functions.The GSH under high water activity is not easy to save, only controlling the water activity below 0.3 to long-term stability.Studies have found that in vitamin C (pH3.3) in aqueous solution containing GSH, with strong reducing effect of vitamin C, GSH no oxidation of solution for the GSSG, but the decomposition speed is accelerated;But in the vitamin C solution GSSG will not change as GSH, and save the stability is very good.And oral intake of GSSG in the upper small intestine can be restored as GSH, in the small intestine epithelial cell surface by gamma GTP (GSH is decomposed into glutamic acid and Cys-Gly) and the role of the dipeptide enzyme and is absorbed, can also play an important physiological function. Glutathione is widely found in animals and plants, and the contents of the bread yeast, wheat germ and animal liver are very high,100~100 mg/1000 g;Content is also rich in human and animal blood, such as human blood contains 26~34 mg/100 g, chicken blood contains 58-73 mg/73 g, pig blood contains 10~15 mg/100 g, the dog blood contains 14~22 mg/100 g.Many vegetables, potato and corn also contains GSH (see table 1). The above information is edited bytongtong of Chemicalbook. |
|
Food additives |
1. join the flour products, can play a role of reduction.Not only make the time of making bread reduced to half of the original or a third, labor conditions greatly improved, and a food nutrition reinforcement and other functions. 2. it added to the yogurt and infant foods, the equivalent of vitamin C, can have the effect of stabilizing agent. 3.to the fish cake, it can prevent the color deepened. 4.added to foods such as meat and cheese, with strong flavor of effect. |
|
Foods rich in glutathione |
Onions, garlic, tomato, fish, shrimp, lamb, peppers. |
|
Reduced glutathione |
Reduced glutathione (GSH) is a kind of important material in the cell, which is composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine, containing sulphur, in order to maintain cell biological functions play an important role, has a variety of biological functions, including participation in the Krebs cycle and sugar metabolism,which is glyceraldehyde triose phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoric acid dehydrogenase coenzyme, to activate a variety of enzymes, promote sugar, fat and protein metabolism, influence the process of cell metabolism;Through the thiol and free radicals in the body and the electronic base,than change into easy metabolic acids substances, accelerate the elimination of the free radicals, and avoid damage to the cell, reduce the toxic effects of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, protect the renal tubules from damage of cisplatinGSH can be used to protect the liver, the synthesis of the liver, the function of the toxin, and the toxin, promote the metabolism of bile acids, which is beneficial to the absorption of fat and fat soluble vitamins. Apply to alleviate chemotherapy, radiation therapy, especially the toxic effects of high-dose chemotherapy;Or for the treatment of all kinds of hypoxemia, such as acute anemia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, etc.;It can be used for liver diseases, including viral, drugs, alcohol and other chemical toxicity caused by the treatment of liver damage.In addition reduced glutathione can also be used for organophosphorus, amino, or aid in the treatment of nitro aromatic compounds poisoning.For acute drug-induced renal injury, uremia, diabetes complications, and also have therapeutic effect of neuropathy. |
|
Antidote |
Glutathione has a broad spectrum of detoxification, which can enter the body with toxic compounds such as acrylonitrile, fluoride, carbon monoxide and heavy metal ions or carcinogens, combining and promote its eduction body outside, of these substances can be used for the treatment of the disease. |
|
Antiallergic agent |
The anti-allergic effect can treat the body acetylcholine, cholinesterase imbalances caused by allergies. |
|
Protect liver agent |
To protect the liver and inhibit the formation of fatty liver function, It not only can be used as a hepatoprotective agent, but also as a feed additive, it can protect the liver of fish and cattle.In aquaculture, because of too close breeding and unclean feed , often lead to liver dysfunction occurs in fishes and cows, adding glutathione can improve liver function. |
|
GSH depletion |
In the combination of glutathione and glutathione, the catalytic activity of glutathione-S-transferase and the combination of exogenous chemicals or their metabolites, which can decrease the toxicity and increase the polarity, is one of the most important methods in the biological transformation.When is suitable for the reaction of exogenous chemicals in large doses, may make the depletion of glutathione, a metabolic saturation (metabolic saturation), and in combined with the amount of time no longer increases with the increase of the exogenous chemicals dosage.The corresponding exogenous chemical toxicity, then the dose-response curve with a low dose not, the poison dynamics is characterized by nonlinear dynamics.GSH depletion mixed order is some kind of exogenous chemicals dosage is too large, also can be due to another foreign competition the combination effect of chemicals, or because of undernutrition or tissue damage that glutathione reduced supplies.GSH depletion have any condition that causes can make the original tolerance dose of poison. |
|
Antioxidants |
Many biochemical reactions in the human body are enzyme catalyzed reactions, most of these enzymes with thiol as active groups, the state of the thiol group determines the activation and inhibition of enzyme activity. Glutathione is natural activator, these enzymes in cells containing sulphur human body cell metabolism can be generated by H2O2 back into H2O, remove free radicals in the body.Free radicals can damage the cell membrane, promote the body's aging, and induce tumor or hardening of the arteries.Of anti peroxidation to human cells, but also can improve the antioxidant ability of skin, make skin burnish.Human aging, infections, poisoning, exogenous toxins, oxidative stress, electrophilic compound attack can be made within the cell plasma GSH level reduces, the phenomenon of apoptosis occurs in very early stage, its degradation process can be observed in the early apoptosis, so it can be observed in the early stage of apoptosis. Glutathione can eliminate lipid oxidation generating , and has the oxidation resistance to grease, still can prevent the sapidity nucleotide (inosinic acid, guanylic acid) food (fish cake, sausage, soy sauce, etc.) of the nucleotide decomposition and lose taste delicious taste. |
|
The preparation of GSH |
Since 1938, the first patent for the use of yeast GSH has been published, and a large number of patent applications have since been published.In general, the preparation methods of GSH are solvent extraction, enzymatic, fermentation and chemical synthesis of four.At present, mainly from the cultivation of high content GSH yeast extract, domestic manufacturers have Shanghai yeast plant and a number of institutions, research units are being developed, foreign manufacturers are BDH, Fluka, J.T.Baker, E.Merck, Haen Riedel-de, Siqma and Japan and the light of the public.The extraction method and enzyme method are mostly wheat germ as raw material, by adding appropriate solvent or combined with amylase, protease treatment, and then by centrifugal, separation and purification. The process flow is simple, see figure 4. Figure 4:The technological process of extraction of glutathione from wheat germ By biotechnology means preparation of glutathione in two ways, one is the selection of high-yielding yeast strains that are rich in GSH, and through the separation system, figure 5 shows a simple technological process.Another way is by cultivating algae that are rich in GSH, extraction is similar to the yeast extract method. Figure 5: The technological process of extraction of glutathione from yeast cell |
|
Uses |
1.Reduced glutathione is a kind of small molecular peptide, a large number of peptides in living organisms, especially in liver cells, protect the liver cell membrane, promote the role of liver enzyme activity, and with a number of toxic chemicals in combination with play the role of detoxification.To the drug poisoning, alcoholism and other causes of liver injury, disease such as cirrhosis of the liver have good curative effect. 2.With antioxidant, scavenging free radicals, detoxification, enhance immunity, anti-aging, anti-cancer, anti radiation damage, and other functions. 3. Used as biochemical reagents,detoxification drugs, it is mainly used for the poisoning of heavy metals, acrylonitrile, fluoride, carbon monoxide and organic solvents. |
|
Description |
Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide (γ-glutamylcysteinylglycine) widely distributed in both plants and animals. GSH serves as a nucleophilic co-substrate to glutathione transferases in the detoxification of xenobiotics and is an essential electron donor to glutathione peroxidases in the reduction of hydroperoxides. GSH is also involved in amino acid transport and maintenance of protein sulfhydryl reduction status. The concentration of GSH ranges from a few micromolar in plasma to several millimolar in tissues such as liver. |
|
Chemical Properties |
White cryst. powder |
|
Originator |
L-Glutathione,Solgar,USA |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A tripeptide compound consisting of glutamic acid attached via its side chain to the N-terminus of cysteinylglycine. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
The tripeptide thiol glutathione (L-γ-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine (GSH)) found in virtually all cells functions in metabolism, transport and cellular protection. Glutathione may be obtained from an yeast or synthetically. A yeast containing 600 parts of yeast solids is heated just to the boiling point of water. The yeast solids are removed by centrifuging or filtration. Sulphuric acid is added to the filtrate to give 0.5 N strength as sulphuric acid 6 parts of ascorbic acid are added. Then 2 parts of cuprous oxide are added with stirring. The reaction mixture is then centrifuged and washed until the precipitate is free from sulphates. The precipitate is suspended in 100 parts of water and hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through the water until all of the copper is precipitated as copper sulphide. The filtrate is evaporated and the glutathione is purified by recrystallization from 50% ethanol. All parts are by weight. The preparation of glutathion by methods of peptide synthesis is expansive and gives 20-30% yield of GHS. For the first time synthetic glutathion was prepared by M. Bergmann et al. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Anabolic, Antidote |
|
benefits |
Glutathione contentin human blood is 26~34mg/100g,scavenging free radical, anti-oxidant, whiteningand spot-removing.Its recommended dosage in skin care products is 0.5~2%. |
|
General Description |
Glutathione (GSH) is the most important nonprotein thiol widely distributed in animal tissues, plants, and microorganisms. GSH is also a key determinant of redox signaling and protection against oxidative stress.Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Endogenous antioxidant that plays a major role in reducing reactive oxygen species formed during cellular metabolism and the respiratory burst. Glutathione-S-transferase catalyzes the formation of glutathione thioethers with xenobiotics, leukotrienes, and other molecules that have an electrophilic center. Glutathione also forms disulfide bonds with cysteine residues in proteins. Via these mechanisms, it can have the paradoxical effect of reducing the efficacy of anti-cancer agents. |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by intravenous route. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx and NOx. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise L-glutathione from 50% aqueous EtOH, dry it in a vacuum and |
InChI:InChI=1/C10H17N3O6S/c11-5(1-2-7(14)15)9(18)13-6(4-20)10(19)12-3-8(16)17/h5-6,20H,1-4,11H2,(H,12,19)(H,13,18)(H,14,15)(H,16,17)
70-18-8 Relevant articles
Rate constant determination for the reaction of hydroxyl and glutathione thiyl radicals with glutathione in aqueous solution
Mezyk, Stephen P.
, p. 8861 - 8866 (1996)
The techniques of pulse radiolysis, lase...
Synthesis of novel chiral bis-N-substituted-hydrazinecarboxamide receptors and probing their solution-phase recognition to chiral carboxylic guests by ESI-TOF/MS and tandem ESI-MS
Nour, Hany F.,Golon, Agnieszka,Islam, Tuhidul,Fernández-Lahore, Marcelo,Kuhnert, Nikolai
, p. 11130 - 11137 (2013)
Seven novel bis-N-substituted-hydrazinec...
Convenient supported recyclable material based on dihydrolipoyl-residue for the reduction of disulfide derivatives
Bienvenu, Céline,Greiner, Jacques,Vierling, Pierre,Giorgio, Christophe Di
, p. 3309 - 3311 (2010)
A quantitative method for the reduction ...
Dissecting the catalytic mechanism of trypanosoma brucei trypanothione synthetase by kinetic analysis and computational modeling
Leroux, Alejandro E.,Haanstra, Jurgen R.,Bakker, Barbara M.,Krauth-Siegel, R. Luise
, p. 23751 - 23764 (2013)
Background: Trypanothione synthetase cat...
Metabolic synthesis of clickable glutathione for chemoselective detection of glutathionylation
Samarasinghe, Kusal T. G.,Munkanatta Godage, Dhanushka N. P.,Vanhecke, Garrett C.,Ahn, Young-Hoon
, p. 11566 - 11569 (2014)
Glutathionylation involves reversible pr...
Kinetic, spectroscopic and in silico characterization of the first step of the reaction between glutathione and selenite
Dereven'kov, Ilia A.,Hannibal, Luciana,Molodtsov, Pavel A.,Branzanic, Adrian M.V.,Silaghi-Dumitrescu, Radu,Makarov, Sergei V.
, (2020)
Reduction of dietary selenite (SeO3H?, S...
Millisecond dynamics in glutaredoxin during catalytic turnover is dependent on substrate binding and absent in the resting states
Jensen, Kristine Steen,Winther, Jakob R.,Teilum, Kaare
, p. 3034 - 3042 (2011)
Conformational dynamics is important for...
Characterization of nucleoside and DNA adducts formed by S-(1-Acetoxymethyl)glutathione and implications for dihalomethane - Glutathione conjugates
Marsch, Glenn A.,Mundkowski, Ralf G.,Morris, Brent J.,Manier, M. Lisa,Hartman, Melanie K.,Guengerich, F. Peter
, p. 600 - 608 (2001)
S-(1-Acetoxymethyl)glutathione (GSCH2OAc...
A New Synthesis of Glutathione via the Thiazoline Peptide
Ozawa, Yoichi,Tsuji, Toshiaki,Ariyoshi, Yasuo
, p. 2592 - 2593 (1980)
A convenient synthesis of glutathione (G...
Simple single-step single-enzyme synthesis of [14C]-GSH
De Keczer, Steve A.,Voronin, Tatyana,Yao, Jennifer,Zhang, Fang-Jie,Masjedizadeh, Mohammad R.
, p. 110 - 112 (2010)
The tri-peptide [14C]-glutathione ([14C]...
Acetone/Isopropanol Photoinitiating System Enables Tunable Disulfide Reduction and Disulfide Mapping via Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Adhikari, Sarju,Yang, Xiaoyue,Xia, Yu
, p. 13036 - 13043 (2018)
Herein, we report the development of a n...
Inhibition of thermus thermophilus HB8 thioredoxin activity by platinum(II)
Kato, Masahiro,Yamamoto, Hitoshi,Okamura, Taka-Aki,Maoka, Nobuko,Masui, Ryoji,Kuramitsu, Seiki,Ueyama, Norikazu
, p. 1023 - 1026 (2005)
A 1 : 1 thioredoxin-Pt(bpy) complex 1 wa...
Structural and biochemical analyses indicate that a bacterial persulfide dioxygenase-rhodanese fusion protein functions in sulfur assimilation
Motl, Nicole,Skiba, Meredith A.,Kabil, Omer,Smith, Janet L.,Banerjee, Ruma
, p. 14026 - 14038 (2017)
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a signaling mo...
Adsorption and orientation of the physiological extracellular peptide glutathione disulfide on surface functionalized colloidal alumina particles
Meder, Fabian,Hintz, Henrik,Koehler, Yvonne,Schmidt, Maike M.,Treccani, Laura,Dringen, Ralf,Rezwan, Kurosch
, p. 6307 - 6316 (2013)
Understanding the interrelation between ...
Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Thiol-Michael Addition Reactions: A Case Study of Reversible Fluorescent Probes for Glutathione Imaging in Single Cells
Chen, Jianwei,Jiang, Xiqian,Carroll, Shaina L.,Huang, Jia,Wang, Jin
, p. 5978 - 5981 (2015)
Density functional theory (DFT) was appl...
Target discovery of ebselen with a biotinylated probe
Chen, Zhenzhen,Jiang, Zhongyao,Chen, Nan,Shi, Qian,Tong, Lili,Kong, Fanpeng,Cheng, Xiufen,Chen, Hao,Wang, Chu,Tang, Bo
, p. 9506 - 9509 (2018)
Despite numerous studies on ebselen over...
Reaction of COTC with glutathione: Structure of the putative glyoxalase I inhibitor
Huntley, C. Frederick M.,Hamilton, Diana S.,Creighton, Donald J.,Ganem, Bruce
, p. 3143 - 3144 (2000)
(matrix presented) The structure of the ...
Development and application of organic reagents for analysis. VIII. Determination of biological thiols with a new fluorogenic thiol-selective reagent, N-(p-[2-(6-dimethylamino)benzofuranyl]phenyl)maleimide.
Nakashima,Nishida,Nakatsuji,Akiyama
, p. 1678 - 1683 (1986)
-
A promiscuous glutathione transferase transformed into a selective thiolester hydrolase
Hederos, Sofia,Tegler, Lotta,Carlsson, Jonas,Persson, Bengt,Viljanen, Johan,Broo, Kerstin S.
, p. 90 - 97 (2006)
Human glutathione transferase A1-1 (hGST...
The thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system can function in vivo as an alternative system to reduce oxidized glutathione in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Tan, Shi-Xiong,Greetham, Darren,Raeth, Sebastian,Grant, Chris M.,Dawes, Ian W.,Perrone, Gabriel G.
, p. 6118 - 6126 (2010)
Cellular mechanisms that maintain redox ...
Electrical 'Wiring' of Glutathione Reductase: an Efficient Method for the Reduction of Glutathione using Molecular Hydrogen as the Reductant
Willner, Itamar,Lapidot, Noa
, p. 617 - 618 (1991)
The enzyme glutathione reductase is chem...
The chemical basis of thiol addition to nitro-conjugated linoleic acid, a protective cell-signaling lipid
Turell, Lucía,Vitturi, Darío A.,Coiti?o, E. Laura,Lebrato, Lourdes,M?ller, Matías N.,Sagasti, Camila,Salvatore, Sonia R.,Woodcock, Steven R.,Alvarez, Beatriz,Schopfer, Francisco J.
, p. 1145 - 1159 (2017)
Nitroalkene fatty acids are formed in vi...
Metal-dependent inhibition of glyoxalase II: A possible mechanism to regulate the enzyme activity
Campos-Bermudez, Valeria A.,Morán-Barrio, Jorgelina,Costa-Filho, Antonio J.,Vila, Alejandro J.
, p. 726 - 731 (2010)
Glyoxalase II (GLX2, EC 3.1.2.6., hydrox...
Visible Light-Mediated Synthesis of Se?S Bond-Containing Peptides
Arsenyan, Pavel,Dimitrijevs, Pavels,Lapcinska, Sindija
supporting information, p. 3968 - 3972 (2021/07/26)
A visible light-initiated method has bee...
Thiolation and Carboxylation of Glutathione Synergistically Enhance Its Lead-Detoxification Capabilities
Sauser, Luca,Mohammed, Tagwa A.,Kalvoda, Tadeá?,Feng, Sheng-Jan,Spingler, Bernhard,Rulí?ek, Lubomír,Shoshan, Michal S.
supporting information, p. 18620 - 18624 (2021/12/13)
The natural tripeptide glutathione (GSH)...
Ethynylation of Cysteine Residues: From Peptides to Proteins in Vitro and in Living Cells
Tessier, Romain,Nandi, Raj Kumar,Dwyer, Brendan G.,Abegg, Daniel,Sornay, Charlotte,Ceballos, Javier,Erb, Stéphane,Cianférani, Sarah,Wagner, Alain,Chaubet, Guilhem,Adibekian, Alexander,Waser, Jerome
supporting information, p. 10961 - 10970 (2020/05/18)
Current approaches to introduce terminal...
70-18-8 Process route
-
![(S)-2-Amino-4-[(R)-1-(carboxymethyl-carbamoyl)-2-(hydroxy-phenyl-methylsulfanyl)-ethylcarbamoyl]-butyric acid](/upload/2023/8/211dce0f-2f06-4166-a7dc-51021c584419.png)
-
(S)-2-Amino-4-[(R)-1-(carboxymethyl-carbamoyl)-2-(hydroxy-phenyl-methylsulfanyl)-ethylcarbamoyl]-butyric acid

-
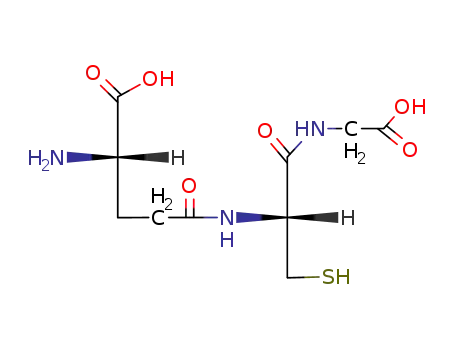
-
70-18-8
GLUTATHIONE

-
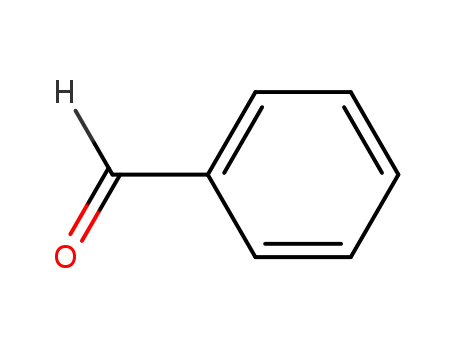
-
100-52-7
benzaldehyde
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
water;
at 25 ℃;
Equilibrium constant;
|
-
-
L-γ-glutamyl->S-((1Ξ,2Ξ)-1,2-dihydroxy-3-phosphonooxy-propyl)-L-cysteinyl->glycine

-
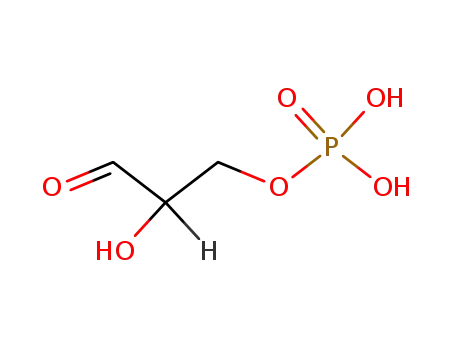
-
142-10-9,591-57-1,20283-52-7,591-59-3
DL-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate

-

-
70-18-8
GLUTATHIONE
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
water;
at 25 ℃;
Equilibrium constant;
|
70-18-8 Upstream products
-
40055-98-9
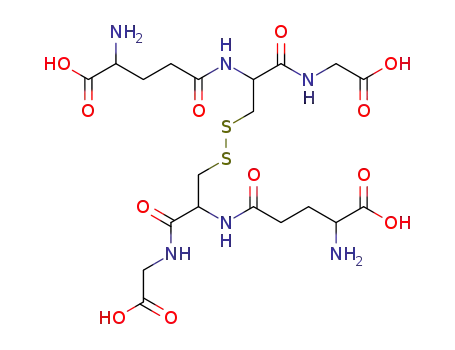
oxidized glutathione
-
27025-41-8
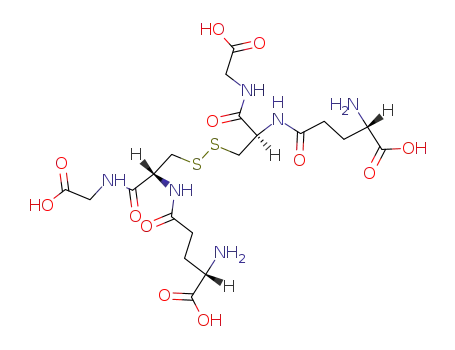
Oxidized glutathione
-
15401-16-8
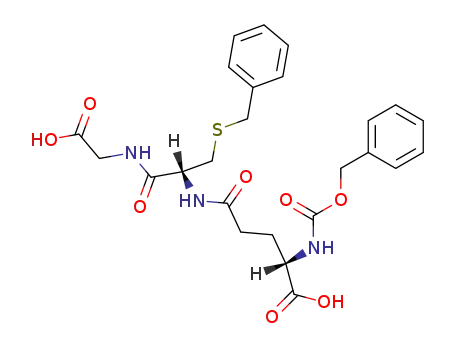
N-[S-benzyl-N-(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-γ-glutamyl)-L-cysteinyl]-glycine
-
52-90-4
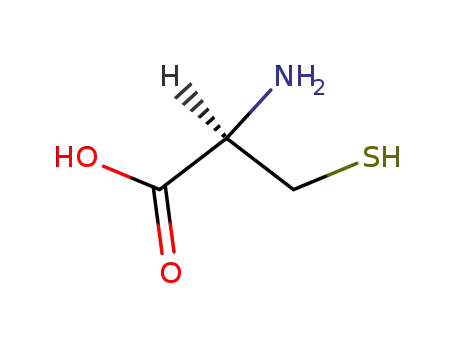
L-Cysteine
70-18-8 Downstream products
-
26289-39-4
S-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)glutathione
-
73322-71-1
S-(4-azidophenacyl)glutathione
-
103-90-2
4-acetaminophenol
-
64889-81-2
S-(5'-Acetamido-2'-hydroxyphenyl)glutathion
Relevant Products
-
Benfotiamine
CAS:22457-89-2
-
Levobupivacaine hydrochloride
CAS:27262-48-2
-
Kojic acid dipalmitate
CAS:79725-98-7